Big Data Doesn't Guarantee Agreement On What Things Mean
Does this sound familiar? You work in a new company and no one agrees on anything? Your business processes seem to run in a haphazard way, that does not yield valid or useful process information? Decision making seems to be ad-hoc at best, or based on incorrect information at worse generated from poorly performing information technology systems. When decisions are made, it doesn't solve problems, it actually creates new ones.
Here's Why Your Executive Information Systems May Be The Issue.

Many companies that have only been in business for a few years are growing rapidly and generating a rapidly growing mountain of data also known as 'Big Data' from their transaction processing systems. Other companies have introduced expert systems within their application software systems, as well as business processes which are being aided by Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. Other critical business functions, such as Project Management, which are inherently risky, are relying on often outdated information, such as labor rates and product costs, which drive incorrect decisions, especially within the human resources management arena.
10 Critical Chain Project Manager Tips
Problematic Information Management Practices
Some companies, due to a lack of coherent information systems, have managed to recreate problems that have been apparent in older, established management information systems for many decades, including:
- Information Silos.
With the rise of cloud based information technology systems, often bought without the coordination of the CIO or even with it, many IT systems contain within them pieces of a bigger puzzle.
For example, most organizations use one of two email systems, Microsoft Outlook or Google Gmail. There is critical information buried in those email servers, yet without the use of proper information system design principles, these common office applications often cannot work together well.
- No Agreed Upon Definition of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
Even some of the most fundamental aspects of your business will lack clarity, for example, what’s a customer? This is a business requirement analysis development issue and a critical KPI Design task.
Information technology, by itself, will not magically determine which KPIs you need to track, nor their meaning when you do figure out what you need to track.
When you are building a data warehouse, which is just another advanced Management Information System tool used by executives to analyze data to make informed decisions, it takes serious time from your human resources team, i.e., the people who run the business, to define a KPI Hierarchy, and to determine how they all fit together to help meet specific goals.
- No Defined Target Solution Architecture.
Many systems, such as SAP ERP, Hubspot Marketing Automation, Zuora Subscription Management and SAP SuccessFactors Human Resources systems must all work together. Just because you can connect them via an API(s) doesn’t mean they are ‘working together’ the way you think they are.
What one calls a Material Master, the other may call an Article Master and there may or may not be agreement as to their true semantic meaning.
Tying all of these disparate systems together is what makes data warehouses such incredibly useful decision support tools.
- Company Master Data is NOT Treated as a Strategic Asset.
Many companies (perhaps most or all) come to know each ‘thing’ by many different identifiers, which has a huge cost to the company, often not measurable directly.
For instance, it is estimated that the U.S economy loses about $3,000,000,000,000.00 USD (3 Trillion) a year due to bad data.
Within each company, there are many data sets, each in its own information system environment, that often represent the same thing, yet often, cause systems analysts to spend hours, days, weeks, or even years reconciling these disparate data sets. For example, Geographic Information Systems very often have issues with location data, such as physical addresses.
- Expensive Strategists Spend 80% of Their Time Gathering Data.
This is just a generally observed phenomena but what it means is that the information architecture has not been designed to avoid this issue.
In this case, it is useful to think of information architecture as about the information itself, versus the physical architecture, such as hard drives, fiber optic cables, wireless networks, data centers, output devices, local area networks, wide area networks, communication technology and all other aspects of your digital information backbone.
That said, this doesn't mean you don't have to consider these things when coming up with an information architecture that supports your business objectives.
- Sales Results.
The answer as to how you did depends entirely on who is being asked to answer the question.
Those siloed information systems are part of this issue as is the lack of agreement, which must be forced downward by top management, if the issue is to be resolved.
Decision support systems which sales management relies on to, for example, determine commission payouts, are beyond critical in importance. Nothing drives sales team turnover higher, faster, than disputes generated by poor quality sales information and sequent commission disputes.
- Business Strategy is Uninformed by the Data.
Balanced Scorecard Practitioners know that having a quantified vision statement, i.e., we want to increase sales by X amount within this time period, requires a robust datawarehouse (a tool) in order to develop a set of KPIs (requires judgement and systems) that can help everyone in the organization achieve their objectives (an outcome) in support of the strategy.
Each business objective should ultimately roll-up to support the overall corporate strategy. Every employee must also be aware of the strategy, understand their role in achieving the objective(s) and how they will be measured. They also must have confidence in the information.
- Data is Required from Many Different Sources in Many Different Formats.
Organizations typically have an 80 20 split (Pareto) between unstructured and structured data.
In order to use the two successfully, the IT organization needs to evaluate, procure and ensure all parts of the organization have the ability to garner useful insights from the torrent of data.
An organization may have, over time, let their information system architecture design "drift", especially when they integrate other devices and computer systems into their system landscape.
One extremely tricky challenge is the introduction of changes to the database management system of your ERP system.
This can induce errors with your organization's information management system software, as well as unintended changes to the actual meaning of the data now coursing through your information system.
Government agencies are also a frequent cause of issues with information systems architecture. For instance, the United States Government (USG) system for sending and receiving import/export information relies on very old, out-of-date technology, which many businesses struggle to work with.
AI technology can also introduce unintended consequences into your data streams. This can be caused by the training data used by the AI, the misunderstanding of the underlying algorithms, and the black box nature of these systems.
- Security Concerns Outweigh Collaboration.
Understandable though it may be, almost all corporate security is designed to keep information secure, which inevitably (but almost always invisibly) leads to users at all levels either not using the systems to their fullest, or worse, simply not attempting to ‘dig deeper’ because they have to seek permission.
Information security analysts typically constrain their security framework design to the concept of SOD or Segregation of Duties, while ignoring the wider implications of their security design upon the dat-to-day performance of people who use information systems subject to such SOD matrixes.
Microsoft Windows often introduces unintended security vulnerabilities into an environment. In the process of 'securing' this system, i.e., installing and maintaining DMZ's, firewalls, and anti-virus software (which requires constant updates to be of any value), unintentional changes as well as limitations are placed on end-users.
This is where the invisible part comes in – most tasks are done ‘in the now’ and when you need to know, you need to know it now.
If it takes hours, days, weeks or months to get the information you need to complete the task at hand, that task typically won’t even be attempted.
This is how information which was very expensive to acquire loses value, which may never show up on the balance sheet.
- Incentive Programs are Completely Misaligned with Corporate Goals.
Incentive programs that are not actually based on achievable metrics, can do far more harm than good.
The best organizations set stretch goals, but then use the information in their datawarehouse, coupled with input from the team regarding what is doable with the present systems, processes and procedures and what they would need to achieve the targets.
Complex Problems
All of these issues need to be solved to enable your Executive Support Systems, Operational Support Systems and Management Support Systems to solve the often challenging business environment encountered around the world. Many businesses, especially large multi-national enterprises that have evolved through acquisitions, will have a separate, unique transaction processing system in each business unit. This can severely complicate the decision making process.
Unit of Measurement Problems
Though the issue of UOM (Unit of Measurement) problems is not typically even thought about, this author, a Senior SAP Project Manager with many full-lifecycle SAP implementations under his belt, has seen this particular issue many times. He has seen many conversion issues related to UOM, such as things like Length, Weight, Volume and Currency conversions. In fact, asa Strategic Enterprise Management Business Consolidation Consultant (SEM BCS), it has surprised me to see how much financial 'slosh' is often bouncing around within large companies due to data conversion problems with weights and foreign currency conversion round-off errors that actually caused by the SAP program itself.
Data Migration Problems
Both during an initial SAP implementation as well as during subsequent acquisitions and divestitures, data migration is often a very complex process that needs to be planned out carefully and thoroughly. Without proper planning and coordination, data migration can become a very expensive exercise with no return on the investment. Most critically, a badly executed data migration process can result in loss of data integrity, and ultimately, cause your financial statements to be incorrect. This can have severe consequences under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
Information Technology Will Evolve Rapidly
As technology continues to advance, the way we manage and store data is also evolving. We are seeing a continued shift towards cloud-based solutions that allow for larger storage capacity, increased scalability, and greater flexibility in how data can be accessed. Additionally, new technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) are being developed that make it possible to automate certain data-related tasks and perform higher-level analytics. As the demand for more complex data management systems increases, organizations will need to find ways to stay ahead of the curve in order to remain competitive and compliant with legal regulations. With the right strategies, IT teams can ensure that their businesses have the most up-to-date and secure solutions available. Furthermore, businesses will need to invest in developing a culture of data-driven decision making in order to capitalize on the potential of their data assets. With the right combination of technology and people power, organizations can create an business environment that prioritizes the collection, analysis, and use of data for business success.
Executive Information Systems

Executive Information Systems (EIS) will evolve to take advantage of the new AI capabilities by giving executives and decision makers access to more comprehensive data than ever before. The ability for EIS systems to use AI to collect and analyze vast amounts of data from multiple sources, allowing users to make more informed decisions quickly and accurately, will be hugely beneficial in the long run. Furthermore, with AI-driven EIS systems also known as an Executive Support System, organizations can gain insights into trends and patterns that may otherwise be difficult to spot or understand. This will ultimately enable them to make more informed decisions and drive better business outcomes. As a result, businesses will become more agile, efficient, and profitable as they leverage AI within their EIS systems.
In addition, the use of AI in EIS systems can also create an enhanced user experience for employees and customers alike. By leveraging AI-driven technology such as natural language processing, machine learning and artificial intelligence, businesses can provide more intuitive solutions that are designed to meet specific customer needs. This will enable them to have greater control over customer interactions, delivering personalized services and experiences that will keep customers coming back for more.
Finally, the use of AI within EIS systems can help companies increase efficiency and accuracy in their operations. With automated processes, businesses can reduce manual labor costs while also increasing speed of service. This will lead to improved productivity levels as well as better customer satisfaction. By utilizing AI-driven systems, companies can ensure that their employees are working smarter, not harder, and that customers are receiving the best possible service. All of this translates into a more rewarding experience for both employees and customers alike.
Overall, leveraging AI within EIS systems provides many advantages to businesses looking to stay ahead in the competitive market. AI-driven systems offer an efficient way to manage tasks and processes, allowing companies to stay on top of their operations while providing better customer service. By taking advantage of these technologies, businesses can remain agile and proactive in their approach, providing a higher level of service and greater satisfaction for both customers and employees alike.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is quickly becoming a major factor in the development and utilization of information systems and enterprise information systems. IoT enables businesses to access, manage, store, and analyze data from multiple sources across different devices and networks. This allows them to obtain better insights into their customers’ behavior, enabling them to make more informed decisions and create better customer experiences. Additionally, by leveraging predictive analytics and automated processes, organizations can achieve greater efficiency and streamline operations. Finally, with the rise of cloud computing technologies, businesses are able to access critical business information quickly, securely, and cost-effectively.
Datawarehouse is the Beating Heart of Your Business
Corporate data warehouses have been in existence, and evolving, for a very long time now. They have been and are being used to make decisions everyday, in businesses, big and small. Yet, knowing what is happening, why it might happen, and then making it happen, remains a challenging task. But decision making driven by an information system you can trust is invaluable.
You Need a Datawarehouse Diagnostic Assessment Tool
For all the previously stated reasons, which represent a synthesis of many years of experience across a multitude of industries which all have specialized information systems, we’ve created a simple diagnostic tool for determining whether you need a datawarehouse, whether your use of it could be improved and how your benchmarks compare to others who completed a similar survey.
Key Tool Output
The output of the tool will look something like this, the difference being it is dynamically updated with your results.
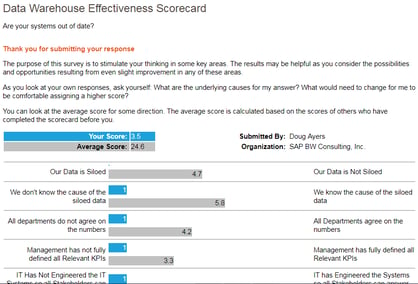
This is an absolutely free online data warehouse diagnostic tool.
Expert Knowledge Available To Diagnose Your Current State
We have done our best to capture the expert knowledge of our team in the development of the business intelligence survey questions.
Business Intelligence Assessment
This BI assessment questionnaire will make you think deeply about your current information systems and how you are using them. But they are questions you must ask if you want to find the answers to your most burning data warehouse usage questions. They are also key inputs to developing a SAP reporting strategy.
Benchmark Yourself Against Competitors and Best Practices
There are no right answers to this, and you can use it as many times as you like as you embark on your improvement journey. There are, however, advantages and disadvantages to different approaches taken when developing computer-based information systems.
Perform Data Driven Cost Benefit Analysis
There are also different cost and benefits to each decision you make with regards to management information systems and managing the digital firm. Just press the button to start your survey.
People Who Read This Also Read:
- Estimate Your SAP BW Consulting Resource Needs Calculator
- 1 Key Tip When Upgrading From SAP BW 3X to SAP BW 7X
- Net Present Value Template
- How To Use A Project Charter To Start A Project Properly
- Fully Load Cost Rate Calcuator
Thanks



