Need a SAP FICO Consultant - We Can Help

Lonnie D. Ayers, PMP
President
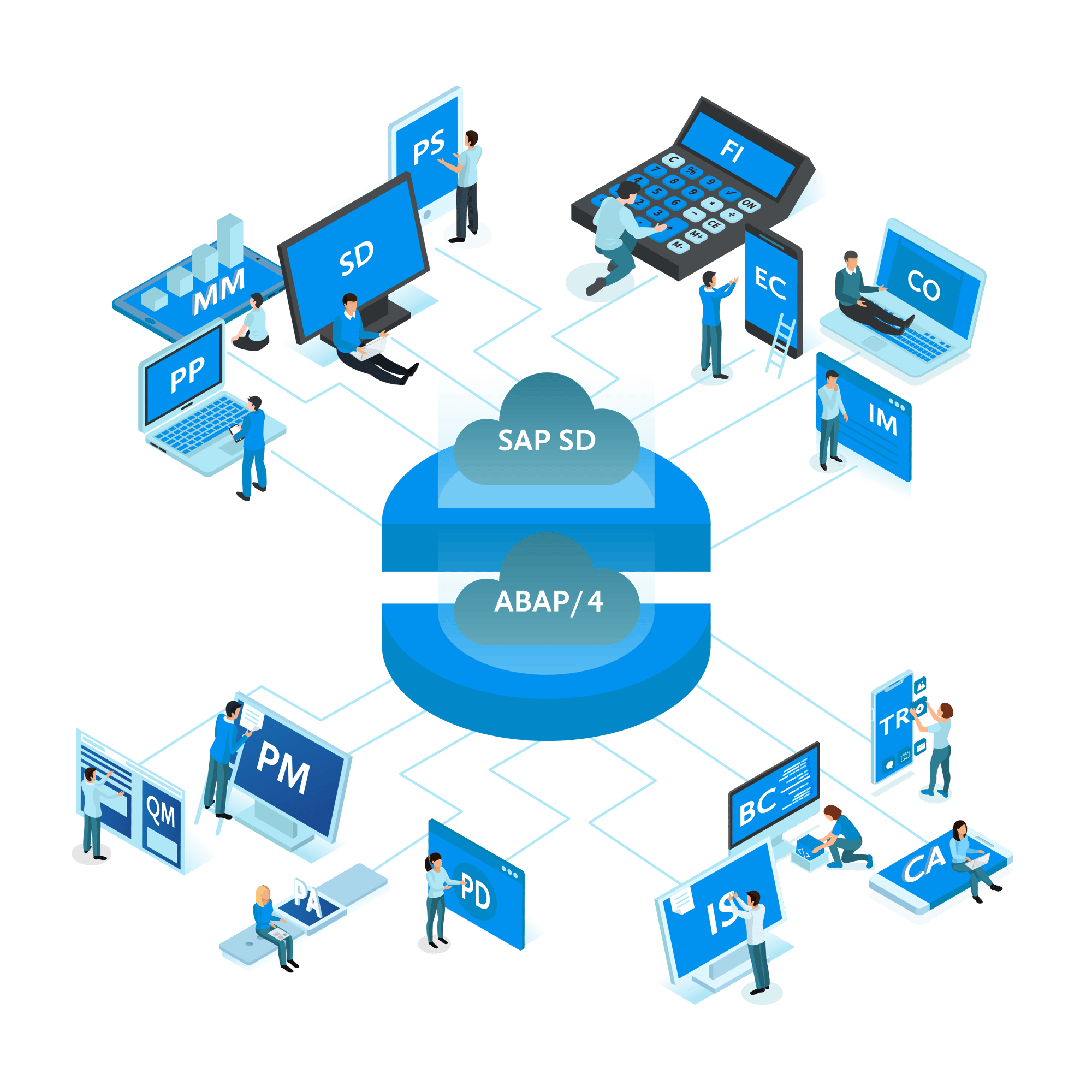
What is SAP FICO
Discover SAP FICO: The Backbone of Financial Management Solutions
SAP FICO, shorthand for SAP Financial Accounting (FI) and SAP Controlling (CO), is the cornerstone of financial management within SAP S/4HANA Finance and the broader SAP ERP ecosystem. It integrates critical processes such as General Ledger (FI-GL), Accounts Payable (FI-AP), Accounts Receivable (FI-AR), Asset Accounting (FI-AA), and Profitability Analysis (CO-PA/Margin Analysis), providing organizations with a single source of truth for financial data.
Beyond core accounting, SAP FICO also connects seamlessly with advanced components such as Treasury and Risk Management (TRM), Bank Communication Management (BCM), and Electronic Bank Statements (EBS MT940 & BAI2) to ensure efficient cash management and compliance. It enables finance teams to support end-to-end Procure-to-Pay (P2P) and Order-to-Cash (OTC) processes, while offering powerful tools for budgeting, forecasting, and Group Reporting/Consolidation.
In essence, SAP FICO empowers businesses to efficiently manage transactions, automate payment runs and reconciliations, and streamline period-end and year-end closing. Leveraging SAP Fiori and SAPUI5 interfaces, users benefit from intuitive reporting dashboards and real-time insights into profitability and performance. Whether you are migrating from ECC to SAP S/4HANA Central Finance or seeking to optimize compliance with IFRS 15/16 revenue recognition through SAP RAR, SAP FICO is your strategic ally in modern financial transformation.
Explore our SAP Consulting Services and Resources to see how SAP FICO can revolutionize your financial management practices and help your organization achieve sustainable growth and profitability.
SAP FICO Consulting
At SAP BW Consulting, Inc., our SAP FICO Consulting Services help organizations maximize the full potential of SAP Financial Accounting (FI) and SAP Controlling (CO) within SAP S/4HANA Finance and Central Finance environments. Our senior consultants bring extensive experience in delivering end-to-end implementations, ECC to S/4HANA migrations, and financial transformation programs across industries such as Automotive, Retail, Manufacturing, and Real Estate.
Core SAP FICO Expertise
We specialize in configuring and optimizing:
-
General Ledger (FI-GL)
-
Accounts Payable (FI-AP)
-
Accounts Receivable (FI-AR)
-
Asset Accounting (FI-AA)
-
Special Purpose Ledger (FI-SPL)
These are extended with advanced components such as Treasury and Risk Management (TRM), Bank Communication Management (BCM), In-House Cash, and Electronic Bank Statements (EBS – MT940 & BAI2) to deliver streamlined cash management, payment automation, and bank reconciliation.
Controlling (CO) Capabilities
Our SAP CO consulting expertise includes:
-
Cost Center Accounting (CO-CCA)
-
Profit Center Accounting (EC-PCA)
-
Internal Orders
-
Product Costing (CO-PC)
-
Profitability Analysis (CO-PA / Margin Analysis)
This ensures real-time profitability insights, accurate allocations, and precise management reporting.
Compliance and Reporting Support
We also provide support for:
-
Revenue Accounting and Reporting (RAR) for IFRS 15/16 compliance
-
Group Reporting and Consolidation
-
Public cloud SAP Finance configurations
With hands-on experience in SAP Fiori and SAPUI5, we simplify financial processes, reduce cycle times, and enable faster month-end and year-end closings.
Global Delivery Model
Whether you need SAP FICO production support, financial close automation with BlackLine integration, or global template rollouts, our consulting team provides the expertise, methodology, and industry knowledge to ensure measurable business value.
By leveraging proven delivery approaches, including onsite–offshore delivery models, we help clients reduce costs, accelerate implementations, and maintain round-the-clock support across geographies.
SAP FICO Configuration
SAP Finance Configuration refers to the process of customizing the SAP Finance and Controlling (FICO) system within SAP S/4HANA Finance or Central Finance to align with the specific business and compliance requirements of an organization. It involves configuring critical components such as General Ledger (FI-GL), Accounts Payable (FI-AP), Accounts Receivable (FI-AR), Asset Accounting (FI-AA), Bank Accounting (FI-BA), and Controlling (CO), as well as leveraging advanced functionality like Electronic Bank Statements (EBS MT940 & BAI2), Bank Communication Management (BCM), and Payment Medium Workbench (DMEE). These activities ensure that the system supports financial operations, reporting, and audit readiness effectively.
To configure the SAP FICO system successfully, several key steps and requirements are involved, including:
Understanding Business Processes
The SAP FICO consultant must thoroughly analyze the organization’s financial processes, such as the Procure-to-Pay (P2P) and Order-to-Cash (OTC) cycles, period-end closing, and compliance reporting requirements. This includes conducting gap analysis, mapping legacy systems, and identifying opportunities for improvement—whether in payment automation, cash pooling, or revenue recognition with SAP RAR.
Defining Organizational Structure
A cornerstone of any SAP S/4HANA implementation involves defining company codes, profit centers, cost centers, and segments for New GL and Universal Journal integration. This step sets the foundation for financial reporting, Group Reporting/Consolidation, and Central Finance deployments, and is typically completed during the blueprint phase.
Chart of Accounts Design
The design of the Chart of Accounts (COA) determines how financial transactions are recorded and reported. Consultants define account groups, assignment models, and mapping tables to ensure accuracy across ledgers. For New GL customers, this also includes segment reporting, document splitting, and intercompany reconciliations.
Chart of Depreciation Design
As part of Asset Accounting (FI-AA) configuration, customers and consultants must adjust the standard Chart of Depreciation to fit business needs. Activities include configuring depreciation areas, asset classes, and fiscal year variants, ensuring smooth asset migration and correct tax reporting during cutover.
Financial Accounting Configuration
The consultant configures document types, posting periods, tolerance groups, subledgers, clearing rules, intercompany transactions, and payment methods. Additional tasks include setting up house banks, automatic payment programs (FBZP), and reconciliation with bank statements (FEBAN). These activities are vital for month-end and year-end closing, audit compliance, and BlackLine integration for financial close automation.
Controlling Configuration
In the CO module, consultants implement Cost Center Accounting (CO-CCA), Profit Center Accounting (EC-PCA), Product Costing (CO-PC), Internal Orders, and Profitability Analysis (CO-PA/Margin Analysis). These configurations provide real-time insights into cost allocations, profitability drivers, and management reporting.
Integration with Other Modules
SAP FICO integrates seamlessly with Materials Management (MM), Sales and Distribution (SD), Project Systems (PS), and Production Planning (PP). Proper integration ensures smooth processes across procurement, inventory management, billing, and project costing.
User Training and Testing
Once configuration is complete, user acceptance testing (UAT) validates that the system meets requirements. Consultants also deliver training and design intuitive SAP Fiori/SAPUI5 dashboards to help end-users adopt new workflows effectively.
In summary, configuring SAP FICO within S/4HANA Finance requires deep expertise, strong collaboration between the client and consultants, and a structured methodology. With careful planning and testing, organizations achieve a fully optimized financial system that supports compliance, profitability analysis, and global financial transformation.
Finance Integration
Finance integration in the context of SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA Finance involves the seamless synchronization of financial data across internal modules and external applications. This ensures accurate, compliant, and comprehensive financial management. At its foundation is the use of T-Accounts, which structure debits and credits for every transaction, supporting period-end closing, reconciliation, and financial statement preparation.
Native Integration Across SAP Modules
Within SAP S/4HANA, all operational modules are natively integrated with Financial Accounting (FI) and Controlling (CO). This means that transactions from Sales and Distribution (SD), Materials Management (MM), Project Systems (PS), and Production Planning (PP) flow automatically into the finance system via the Universal Journal.
-
In the railroad industry, revenue from ticket sales, procurement of track materials, and locomotive capital projects post directly into General Ledger (FI-GL), Accounts Payable (FI-AP), Accounts Receivable (FI-AR), and Asset Accounting (FI-AA).
-
In the retail industry, finance integration also supports specialized closing cycles such as the Retail Calendar (4-4-5), which standardizes financial periods to align with seasonal sales, inventory turnover, and reporting requirements.
Treasury and External Integration
Beyond SAP’s internal modules, finance integration extends to Treasury and Cash Management. SAP FICO consultants configure tools such as:
-
Bank Communication Management (BCM)
-
Electronic Bank Statements (EBS MT940/BAI2)
-
Payment Medium Workbench (DMEE)
These enable automation of vendor payments, customer collections, intercompany settlements, interbank loan transfers, and cash pool sweeps. In industries like railroads and retail, these integrations ensure real-time visibility into liquidity, payroll, and vendor settlements.
Driving Financial Transparency
Finance integration also ensures end-to-end transparency and compliance. By embedding processes such as:
-
Revenue Accounting and Reporting (RAR) for IFRS 15/16 compliance
-
Profitability Analysis (CO-PA/Margin Analysis)
-
Group Reporting and Consolidation
organizations meet global accounting standards while gaining real-time visibility into performance. For example, railroads can track fuel, track maintenance, and wages, while retailers can monitor seasonal profitability trends using the 4-4-5 retail calendar.
Enhanced Decision-Making
When combined with SAP Fiori dashboards and BlackLine financial close automation, finance integration simplifies reporting, accelerates decision-making, and improves cash flow management. This provides CFOs and business leaders with the insight to optimize both short-term operations and long-term strategic planning.
In summary, SAP Finance integration forms the backbone of effective financial management by connecting ERP processes, Treasury systems, and external applications into one unified financial platform. By incorporating specialized industry requirements such as the retail 4-4-5 calendar and global treasury functions, organizations enhance compliance, efficiency, and profitability across the enterprise.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory Mandated Financial Management Requirements are Constantly Changing
In today’s global business environment, regulatory compliance in SAP FICO consulting ensures that the SAP Finance and Controlling (FI/CO) system is configured to meet evolving financial reporting standards, tax requirements, and audit regulations. For industries such as pharmaceuticals, medical devices, automotive, and financial services, compliance is not optional — it is critical to sustaining operations and protecting brand integrity.
GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles)
For U.S.-based companies, SAP FICO consultants configure General Ledger, Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, and Asset Accounting to ensure GAAP-compliant reporting. This includes:
-
Accurate revenue recognition (RAR/IFRS 15)
-
Expense recognition and allocations
-
Asset valuation and Financial Statement Versioning (FSV)
IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards)
In multinational organizations, consultants configure Central Finance, Group Reporting, and Consolidation within SAP S/4HANA Finance to support IFRS compliance. This requires:
-
Handling multi-currency transactions
-
Managing parallel ledgers and segment reporting in New GL/Universal Journal
-
Applying consolidation adjustments for transparency across subsidiaries
-
Ensuring IFRS 9 readiness for financial instruments, particularly around classification, measurement, and impairment reporting
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
Publicly traded companies must adhere to SOX requirements, which mandate robust internal controls, audit trails, segregation of duties, and workflow approvals. Using tools like SAP Access Control (GRC), Bank Communication Management (BCM), BlackLine integration, or SAP SEM BCS and SAP BPC, consultants ensure data integrity and reporting accuracy.
FDA & Healthcare Regulations (FDA, HIPAA)
In industries like pharmaceuticals and healthcare, compliance extends to FDA reporting requirements and HIPAA data privacy standards. SAP FICO consultants configure:
-
Secure audit trails
-
Encryption and role-based access controls
-
Workflow approvals for clinical and financial data
Specialized scenarios include Revenue Accounting for Clinical Trials, where consultants ensure that revenue recognition aligns with trial milestones, FDA submission cycles, and financial reporting requirements.
ISO Standards & ESG Reporting
Organizations also seek compliance with ISO quality, environmental, and information security standards. SAP CO capabilities, including Product Costing (CO-PC) and Profit Center Accounting (EC-PCA), align financial and operational data for certification processes.
Increasingly, SAP FICO also supports ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) reporting, enabling companies to comply with emerging sustainability disclosure requirements.
In summary, SAP FICO consultants configure financial systems to remain compliant with GAAP, IFRS, IFRS 9, SOX, FDA, HIPAA, ISO, and ESG mandates. By leveraging S/4HANA Finance, Central Finance, RAR, Group Reporting, and integrated Treasury tools, organizations mitigate compliance risk, streamline audits, and maintain public trust through accurate, transparent, and industry-specific financial reporting.
Financial Planning Process
The Financial Planning Process in SAP is a structured approach to forecasting, budgeting, consolidation, and performance analysis that enables organizations to align financial strategies with business objectives. Within SAP S/4HANA Finance, this process integrates seamlessly with SAP BPC (Business Planning and Consolidation), SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC), and SAP BW/4HANA, providing a single platform for planning, reporting, and compliance.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how SAP FICO consultants support the financial planning lifecycle:
Strategic Planning
The process begins with defining long-term business objectives and financial targets. SAP FICO consultants collaborate with executives to align strategic planning, Group Reporting, and Central Finance initiatives with financial goals, ensuring consistency across local GAAP, IFRS, and management reporting standards.
Budgeting and Forecasting
Using SAP BPC and SAP S/4HANA Planning modules, consultants design budgeting and forecasting models that incorporate General Ledger (FI-GL), Profitability Analysis (CO-PA/Margin Analysis), and Cost Center Accounting (CO-CCA). Forecasts can include cash flow planning, P&L simulations, and balance sheet projections, enabling organizations to anticipate financial performance under varying conditions.
Data Collection and Aggregation
SAP FICO consultants consolidate data from SD (Sales and Distribution), MM (Materials Management), PP (Production Planning), and HR/Payroll systems, while also integrating with BlackLine and external analytics platforms to ensure accuracy in financial projections. They configure mapping tables and reconciliation processes to unify data into the Universal Journal for real-time reporting.
Scenario Planning
Through SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC), consultants enable advanced what-if analysis, sensitivity testing, and simulation modeling. This allows companies to evaluate the financial impact of changes in market conditions, capital expenditures, or global operations. For example, scenario planning may assess how changes in interest rates, currency fluctuations, or supply chain disruptions affect profitability.
Financial Modeling and Analysis
With SAP BW/4HANA and SAC dashboards, consultants design models that analyze variance reporting, KPIs, and margin analysis. These tools provide actionable insights into cost drivers, product profitability, and segment reporting within the New GL/Universal Journal, enabling faster decision-making at the CFO level.
Collaboration and Review
The planning process is inherently cross-functional. SAP FICO consultants facilitate collaboration between finance, operations, sales, and supply chain teams. Using SAP Fiori and SAPUI5 interfaces, stakeholders gain real-time visibility into budgets and forecasts, streamlining review cycles and reducing reliance on manual spreadsheets.
Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
SAP FICO consultants implement real-time dashboards, alerts, and automated reporting workflows to monitor performance against budget. With integrations to Treasury (TRM), Bank Communication Management (BCM), and Electronic Bank Statements (EBS), organizations gain cash flow visibility and can adjust plans dynamically to meet evolving market and compliance requirements.
In summary, the Financial Planning Process in SAP combines SAP BPC, SAC, BW/4HANA, and FICO configuration to deliver a comprehensive platform for budgeting, forecasting, scenario analysis, and financial consolidation. By leveraging these tools, consultants empower organizations to achieve data-driven planning, compliance with GAAP/IFRS, and improved profitability through real-time financial insights.
Financial Close Process
The Financial Close Process is like tidying up a messy room before guests arrive. Just as you organize and make everything presentable, the financial close ensures all transactions are accurately recorded, reconciled, and prepared for reporting. Within SAP S/4HANA Finance, this process is supported by advanced capabilities in General Ledger (FI-GL), Accounts Payable (FI-AP), Accounts Receivable (FI-AR), Asset Accounting (FI-AA), and Controlling (CO), ensuring complete transparency and compliance.
Steps in the Financial Close Process (Airline Industry Example)
Transaction Recording
Throughout the accounting period, transactions such as ticket sales, fuel purchases, maintenance costs, and payroll must be recorded accurately. SAP FICO consultants configure FI-GL, FI-AP, FI-AR, and FI-AA to capture these entries. They also leverage integration with Sales and Distribution (SD), Materials Management (MM), and Payroll systems to ensure postings flow seamlessly into Finance.
Reconciliation
Before closing the books, accounts must be reconciled. This involves comparing SAP records with bank statements, credit card settlements, and vendor/customer accounts. Using tools like Electronic Bank Statements (EBS – MT940/BAI2), Lockbox Processing, and Search Strings in FEBAN for auto reconciliation, consultants streamline matching and eliminate manual errors.
Adjustments and Accruals
To reflect the true financial position, adjustments and accruals are configured within New GL and Universal Journal. Consultants automate processes for intercompany transactions, recurring entries, depreciation runs, and top-down distributions in CO-PA, ensuring accurate recognition of revenues and expenses.
Closing Entries
At period-end, closing activities such as clearing temporary accounts, posting depreciation, and reconciling intercompany balances are executed. SAP FICO consultants design Financial Statement Versions (FSV), configure tolerance groups, posting periods, and allocations, and leverage BlackLine financial close automation to accelerate the cycle.
Financial Reporting
After closing, financial statements—income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement—are generated. SAP consultants enhance reporting with SAP Group Reporting, SAC (SAP Analytics Cloud), and AO (Analysis for Office), ensuring compliance with GAAP, IFRS, and SOX. Real-time dashboards built in SAP Fiori/SAPUI5 give CFOs immediate insight into profitability and performance.
Consultant Role in SAP FICO Close
SAP FICO consultants play a critical role by:
-
Configuring SAP modules for accurate transaction capture.
-
Automating reconciliations, accruals, and closing entries.
-
Supporting year-end and period-end closing activities across global entities.
-
Collaborating with finance, IT, and operations to align close calendars and deliver timely results.
-
Leveraging AIF Monitoring, mapping tables, and LSMW for data validation and cutover activities during system conversions or migrations.
In summary, the Financial Close Process in SAP FICO ensures financial records are accurate, transparent, and compliant. With capabilities like EBS, Lockbox, BlackLine integration, Group Reporting, and SAC dashboards, organizations accelerate close cycles, reduce compliance risk, and provide reliable information to drive strategic decisions.
Financial Reporting
Financial reporting in the petroleum industry, particularly for global exploration companies like Saudi Aramco, is essential for communicating performance, position, and future outlook to stakeholders such as investors, regulators, and management. Its purpose is to deliver transparent, accurate, and compliant financial information—covering revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, and cash flows—so stakeholders can assess the company’s health and make informed decisions.
Configuring SAP Financial Reporting
Within SAP S/4HANA Finance, the SAP FICO consultant configures reporting processes to ensure accuracy, compliance, and flexibility:
Configuring Financial Statement Formats
Consultants design Financial Statement Versions (FSV) to generate key reports such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. These reports are tailored to GAAP, IFRS, and SOX standards, and can be enhanced with Report Painter/Writer, SAP Query, and Drill-Down Reports for deeper analysis.
Establishing Reporting Hierarchies
Reporting hierarchies are built using profit centers, cost centers, and segments in New GL/Universal Journal. Consultants configure margin analysis (CO-PA), cost allocations (assessments/distributions), and overhead costing cycles to provide management with actionable profitability insights across exploration projects, subsidiaries, and regions.
Implementing Consolidation Processes
For companies with global operations, SAP FICO consultants implement Group Reporting and Consolidation within S/4HANA. This includes currency translation, intercompany elimination, consolidation adjustments, and IFRS 9 readiness for financial instruments. Integration with SAC (SAP Analytics Cloud) and Analysis for Office (AO) enables real-time consolidated reporting for CFOs and investors.
Examples of Key Financial Reports
-
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
Summarizes revenues, expenses, and net income. In petroleum, this includes oil & gas sales revenue, exploration costs, and overall profitability. -
Balance Sheet
Provides a snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity at a point in time. For exploration firms, this may include oil reserves, capital equipment, and debt obligations, along with adjustments for environmental and compliance liabilities. -
Cash Flow Statement
Tracks inflows/outflows across operating, investing, and financing activities. In SAP, consultants configure cash flow reporting integrated with Treasury (TRM), Bank Communication Management (BCM), and Electronic Bank Statements (EBS MT940/BAI2) to deliver real-time visibility into liquidity, exploration investments, and debt repayments.
Consultant Role in SAP Reporting
SAP FICO consultants play a pivotal role by:
-
Configuring FSV, Universal Journal, and profitability reporting.
-
Enabling variance reporting, top-down distributions in CO-PA, and consolidation adjustments.
-
Automating reporting with BlackLine integration and SAC dashboards.
-
Supporting audit trails and compliance with GAAP, IFRS, SOX, and industry regulations.
In summary, financial reporting within the petroleum industry—and other complex global sectors—relies on SAP S/4HANA Finance, Group Reporting, Treasury, and Analytics tools. By configuring these processes, SAP FICO consultants ensure transparency, accountability, and investor confidence while enabling organizations to manage financial resources effectively.
Cross-Functional Analysis
Cross-functional analysis is the process of examining and connecting data, processes, and interactions across departments to improve performance and achieve strategic objectives. In the context of SAP FICO consulting, it means analyzing how financial data intersects with operations, sales, procurement, and HR—revealing the full impact of decisions on profitability and growth.
Setting Up Cross-Functional Analysis in SAP
Define Objectives
The SAP FICO consultant works with stakeholders to define objectives such as improving profitability analysis (CO-PA/Margin Analysis), reducing costs, or enabling IFRS- and GAAP-compliant reporting across the enterprise.
Identify Data Sources
Relevant data comes from SAP modules such as FI/CO, SD, MM, PP, and HR/Payroll, and from ancillary solutions like Ariba, Concur, FieldGlass, Vistex, Paymetrics, and Maximo. Consultants ensure that this information flows into the Universal Journal for consistency and accuracy.
Data Mapping and Integration
Consultants leverage LSMW (Legacy System Migration Workbench), IDocs/ALE/XI interfaces, and AIF monitoring to map and integrate financial and operational data across systems. They also configure mapping tables for source/target reconciliation, ensuring accuracy when migrating from ECC to S/4HANA Finance or Central Finance.
Data Analysis and Visualization
With tools like SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC), Analysis for Office (AO), and SAP BW/4HANA, consultants create dashboards and reports to identify trends across functions. Report Painter, Report Writer, SAP Query, and ALV reports are also used for variance and drill-down analysis.
Identify Key Insights
Insights may include process bottlenecks in Procure-to-Pay (P2P) or Order-to-Cash (OTC), inefficiencies in intercompany transactions or cash pooling, or opportunities for cost optimization through product costing and overhead allocation cycles. Consultants apply root cause analysis and provide clear recommendations.
Recommendations and Action Plan
Based on findings, consultants may recommend process redesign, system enhancements, or automation via SAP Fiori/SAPUI5 apps to streamline workflows. These actions align financial KPIs with operational goals for maximum impact.
Implementation and Monitoring
Consultants support implementation through Agile or Waterfall methodologies (Jira, HP-ALM, Wrike), train business users, and monitor KPIs. They often serve as the SPOC (Single Point of Contact) in onsite-offshore delivery models, ensuring continuous support, after action reviews, and post-implementation improvements.
Outcomes and Benefits
| Outcome | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Improved Decision-Making | Informed strategic choices supported by real-time profitability and compliance data |
| Enhanced Efficiency | Streamlined cross-functional processes, reduced costs, optimized allocations |
| Better Customer Experience | Faster, more accurate reporting, enabling improved services and customer satisfaction |
| Increased Agility | Early identification of risks and opportunities through scenario planning and variance analysis |
Management Accounting
Management accounting focuses on providing internal stakeholders—executives, managers, and decision-makers—with the financial and non-financial insights they need for planning, control, and performance evaluation. By analyzing costs, profitability, and operational data, management accounting supports strategic decision-making and resource optimization across industries.
Within SAP Financial and Controlling (FICO) in S/4HANA Finance, management accounting is strengthened by advanced functionalities in Controlling (CO), Treasury, and Group Reporting, enabling organizations to connect cost data with profitability and compliance requirements.
Cost Accounting and Cost Management
SAP FICO captures and allocates costs through Cost Center Accounting (CO-CCA), Internal Orders, Activity-Based Costing, and Product Costing (CO-PC). Consultants also configure overhead allocation cycles, assessments, and distributions, ensuring costs are accurately traced back to products, projects, or business units.
-
In heavy equipment manufacturing, this enables OEMs to track direct materials, labor, and overhead, while using top-down distributions in CO-PA Margin Analysis to analyze profitability by region or product line.
-
In aviation MRO services, management accounting integrates with Intercompany Configurations to allocate costs across subsidiaries and assess profitability of long-term service contracts.
Budgeting and Variance Analysis
Through budgeting, forecasting, and variance reporting in SAP FICO, organizations compare actual performance against planned targets. Variance analysis identifies cost overruns, inefficiencies, or underutilized resources. Consultants configure SAP Financial Statement Versions (FSV), Universal Allocation in S/4HANA, and Consolidation Adjustments to ensure accurate reporting at both entity and group levels.
-
Manufacturing companies leverage this to fine-tune resource allocation and pricing strategies.
-
MRO providers gain transparency in cost variances across aircraft fleets, enabling corrective actions in resource deployment or contract pricing.
Treasury and Intercompany Processes
Management accounting also relies on Treasury integration for cash flow planning and intercompany settlements. SAP consultants configure:
-
Central Payments in S/4HANA to streamline payment processing across multiple company codes.
-
Inter Bank Loan Transfers and Cash Pool Sweeps to optimize liquidity management across global subsidiaries.
-
Automated reconciliations with Bank Communication Management (BCM) and Electronic Bank Statements (EBS MT940/BAI2) to improve accuracy and reduce manual effort.
These treasury-driven capabilities provide finance leaders with real-time visibility into group cash positions and working capital efficiency.
In summary, SAP FICO supports management accounting by combining cost accounting, variance analysis, product costing, overhead allocations, treasury integration, and intercompany processes. By leveraging features such as Central Payments, Cash Pool Sweeps, Inter Bank Loan Transfers, and Consolidation Adjustments, organizations enhance profitability analysis and maintain compliance with global reporting standards. This empowers leaders in industries like heavy manufacturing and aviation MRO to make smarter, data-driven decisions that drive sustained growth and competitiveness.
Financial Integration Architecture
Financial Integration Architecture refers to the overarching design and framework that governs how financial systems, processes, and data are interconnected and interact within an organization. It encompasses the structural components, technologies, standards, and protocols used to integrate various financial systems, applications, and interfaces to ensure seamless communication and data exchange.
In the context of SAP FICO consulting, the Financial Integration Architecture serves as the blueprint for designing, implementing, and optimizing financial systems and interfaces to support the organization's business objectives and requirements. It includes components such as:
-
System Architecture: This defines the overall structure and layout of financial systems, including SAP ERP modules (such as FI, CO, AA, AP, and AR), third-party applications, databases, and middleware platforms.
-
Data Architecture: This encompasses the organization's data model, data flows, data storage, and data governance practices, ensuring data consistency, accuracy, and integrity across financial systems and interfaces.
-
Integration Architecture: This outlines the integration patterns, protocols, APIs, and middleware solutions used to connect disparate financial systems, applications, and external partners, facilitating real-time data exchange and process automation.
-
Security Architecture: This addresses security controls, authentication mechanisms, encryption standards, and access policies to protect sensitive financial data and prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
-
Scalability and Performance Architecture: This focuses on designing financial systems and interfaces to handle increasing volumes of transactions, users, and data without compromising performance or reliability.
Diagnosing issues with the existing Financial Integration Architecture is a critical step in designing a better one. The expertise of the SAP FICO Solution Architect comes into play in several key areas:
-
Assessment and Analysis: The Solution Architect conducts a comprehensive assessment of the organization's existing financial systems, interfaces, and integration architecture. This includes identifying pain points, bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
-
Root Cause Analysis: The Solution Architect performs root cause analysis to understand the underlying factors contributing to integration issues, data inconsistencies, and performance challenges within the financial systems landscape.
-
Gap Analysis: The Solution Architect conducts a gap analysis to compare the organization's current Financial Integration Architecture against industry best practices, standards, and emerging technologies. This helps identify gaps, shortcomings, and areas where enhancements are needed.
-
Recommendations and Roadmap: Based on the assessment findings and analysis, the Solution Architect develops recommendations and a strategic roadmap for designing and implementing a better Financial Integration Architecture. This may include technology upgrades, process improvements, organizational changes, and investment priorities.
-
Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement: The Solution Architect collaborates closely with stakeholders, including finance leaders, IT professionals, business users, and external partners, to gain insights, gather requirements, and align on the vision and goals for the new Financial Integration Architecture.
By leveraging the expertise of the SAP FICO Solution Architect and following best practices in Financial Integration Architecture design, organizations can optimize their financial systems, enhance operational efficiency, and drive business growth in today's interconnected and digitally-driven landscape. This sets the stage for addressing financial interfaces and bank account integration, ensuring a holistic and integrated approach to financial management and data exchange within the organization.
Financial Interfaces
Developing financial interfaces with the SAP FICO system involves a systematic process to ensure seamless integration and data exchange between SAP FICO and other internal or external systems. Here's a step-by-step process for identifying, specifying, documenting, developing, testing, and deploying financial interfaces:
-
Identification of Interface Requirements:
- The SAP FICO consultant collaborates with stakeholders to identify interface requirements, including data sources, data formats, frequency of data transfer, and business rules governing data exchange.
- Stakeholders may include finance, IT, operations, and external partners or vendors.
-
Specification and Documentation:
- The consultant documents detailed specifications for the interface, including data mappings, transformation rules, error handling procedures, and interface protocols.
- Standards such as XML, JSON, EDI, or proprietary formats may be used for data exchange, depending on the requirements.
-
Interface Development:
- Based on the specifications, the interface is developed using appropriate tools, programming languages, and integration platforms.
- The consultant ensures that the interface adheres to coding standards, best practices, and security protocols to safeguard data integrity and confidentiality.
-
Testing and Validation:
- The developed interface undergoes rigorous testing to validate its functionality, accuracy, and reliability.
- Various testing scenarios are executed, including positive and negative testing, boundary testing, and end-to-end testing to simulate real-world usage conditions.
- Data reconciliation and error handling mechanisms are tested to ensure robustness and resilience of the interface.
-
User Acceptance Testing (UAT):
- The interface is presented to end-users and stakeholders for UAT, where they validate its performance, usability, and alignment with business requirements.
- Feedback and issues identified during UAT are addressed and resolved before proceeding to deployment.
-
Deployment and Rollout:
- Once the interface passes testing and UAT, it is deployed into the production environment using the approved Change and Transport Management System via the Solution Manager.
- The consultant oversees the deployment process, ensuring minimal disruption to operations and adherence to change management procedures.
- Post-deployment activities may include monitoring, performance tuning, and user training to ensure smooth operation and adoption of the interface.
The critical role of the SAP FICO consultant in this process includes:
- Understanding business requirements and translating them into technical specifications.
- Developing interfaces that are efficient, scalable, and maintainable.
- Ensuring compliance with industry standards, data privacy regulations, and security protocols.
- Collaborating with stakeholders and IT teams to address integration challenges and resolve issues.
The outcome and benefits of developing and having financial interfaces with the SAP FICO system include:
| Outcome | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Seamless Data Exchange | - Real-time access to accurate and consistent financial data |
| - Improved decision-making and financial visibility | |
| Enhanced Operational Efficiency | - Automated data transfer and reduced manual effort |
| - Streamlined business processes and faster response times | |
| Improved Data Integrity and Accuracy | - Reduced risk of data errors, duplication, and inconsistency |
| - Enhanced compliance with regulatory requirements | |
| Increased Business Agility | - Ability to adapt quickly to changing business needs |
| - Facilitated integration with new systems and technologies |
By following a structured approach to interface development and leveraging the expertise of SAP FICO consultants, organizations can achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and agility in their financial operations, enabling them to stay competitive and responsive in today's dynamic business environment.
Bank Account Integration
Integrating the SAP Financial System with the company's bank accounts is crucial for automating financial transactions, streamlining payment processes, and ensuring accurate cash management. The integration facilitates the flow of financial data and transactions between SAP modules, external systems, and banking institutions, enabling efficient handling of payroll, payments, collections, and liquidity management.
-
Integration with SAP Human Resources Management System (HRMS) - Payroll:
- In the payroll process, employee salaries, wages, taxes, and deductions are calculated and processed within the SAP HRMS module.
- Once payroll processing is complete, the SAP Financial System is integrated with the company's bank accounts to initiate direct deposits or issue checks to employees.
- The integration ensures that payroll transactions are accurately recorded in the financial system and reflected in the company's bank statements.
-
Payment Processing and Payment Gateways:
- The SAP Financial System integrates with payment processing platforms and payment gateways to facilitate electronic payments, including vendor payments, supplier invoices, and employee expense reimbursements.
- Payment files generated within SAP are transmitted to the bank electronically via secure channels such as Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) or Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).
- Payment gateways enable seamless processing of online payments, credit card transactions, and e-commerce transactions, with real-time synchronization of payment data between SAP and the banking system.
-
Commercial Paper (Bonds) Integration:
- For companies issuing commercial paper or bonds, SAP Financial System integrates with investment banks and financial institutions to manage bond issuances, interest payments, and redemptions.
- Integration ensures accurate tracking of bond issuance proceeds, interest accruals, and redemption schedules, with compliance with regulatory requirements such as SEC filings in the United States or European Central Bank reporting in Europe.
Differences in US Bank Integration vs European Bank Integration Regulations:
-
Regulatory Compliance: In the United States, bank integration is subject to regulations such as the Electronic Funds Transfer Act (EFTA), Regulation E, and the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC). These regulations govern electronic payments, wire transfers, and consumer protection in banking transactions. In Europe, bank integration is governed by the Payment Services Directive (PSD2) and the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) regulations, which aim to standardize payment systems, enhance security, and promote competition in the banking sector.
-
Payment Formats: US banks typically use Automated Clearing House (ACH) for electronic payments and wire transfers for high-value transactions. European banks follow SEPA standards for Euro-denominated payments and use SWIFT messaging for international transactions.
-
Data Privacy and Security: Both US and European banks adhere to strict data privacy and security regulations, such as the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) in the US and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. These regulations govern the protection of sensitive financial data, customer privacy, and cybersecurity measures.
- House Bank: The SAP Financial Management System also provides the ability to set up a House Bank, which allows businesses with complex ownership structures to successfully manage the various financial flows of their subsidiaries.
In summary, integrating the SAP Financial System with the company's bank accounts and payment systems enables seamless financial transactions, improved cash visibility, and enhanced regulatory compliance. Whether in the US or Europe, adherence to regulatory requirements, standardization of payment formats, and robust data security measures are essential for successful bank integration and efficient financial operations.
Real-Time Insights
Real-Time Insights refer to the ability to access, analyze, and act upon up-to-date financial and operational data as it becomes available within the SAP Financial System. These insights provide decision-makers with timely information and visibility into key performance indicators, trends, and anomalies, enabling them to make informed decisions, identify opportunities, and mitigate risks proactively.
Real-Time Insights are important for several reasons:
-
Timely Decision-Making: With real-time access to financial data and performance metrics, stakeholders can make informed decisions quickly, responding to changing market conditions, customer demands, and competitive pressures with agility.
-
Enhanced Visibility and Transparency: Real-time insights provide stakeholders with a clear and comprehensive view of the organization's financial health, operational performance, and business trends, fostering transparency and accountability across the enterprise.
-
Proactive Risk Management: By monitoring key indicators and metrics in real-time, organizations can identify potential risks and issues early on, allowing them to implement corrective actions and risk mitigation strategies before problems escalate.
-
Opportunity Identification: Real-time insights enable organizations to identify emerging opportunities, market trends, and customer preferences, enabling them to capitalize on new business opportunities and stay ahead of the competition.
The SAP Business Warehouse (BW) plays a crucial role in enabling real-time insights by providing a centralized platform for data integration, storage, and analysis. BW aggregates data from various SAP modules, external systems, and sources, enabling users to perform complex analyses, generate reports, and visualize insights in real-time.
Having real-time insights provides a competitive advantage to SAP customers by:
- Empowering decision-makers with timely and actionable information for strategic planning, resource allocation, and performance optimization.
- Improving operational efficiency and effectiveness through data-driven decision-making and process optimization.
- Enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty by enabling organizations to respond quickly to customer needs and preferences.
- Driving innovation and agility by fostering a culture of continuous improvement and adaptation to changing market dynamics.
The role of the SAP FICO consultant in ensuring clients have real-time insights is multifaceted:
-
Data Governance and Quality Assurance: The consultant ensures that data integrity, accuracy, and consistency are maintained across the SAP Financial System, BW, and other integrated systems. This involves implementing data validation rules, data cleansing processes, and data quality checks to ensure reliable insights.
-
Security and Access Control: The consultant implements robust security measures and access controls to protect sensitive financial data and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, including segregation of duties (SoD) and role-based access controls (RBAC). This ensures that only authorized users have access to real-time insights and sensitive financial information.
-
Configuration and Optimization: The consultant configures and optimizes the SAP Financial System and BW to enable real-time data integration, analysis, and reporting. This may involve optimizing data extraction and loading processes, designing efficient data models, and tuning performance parameters to ensure timely delivery of insights.
-
User Training and Support: The consultant provides training and support to end-users and stakeholders on how to effectively leverage real-time insights for decision-making and performance management. This includes training on BW reporting tools, dashboard creation, and data visualization techniques.
The outcomes and benefits of having real-time insights include:
| Outcome | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Timely Decision-Making | - Quick response to market trends and competitive threats |
| - Improved strategic planning and resource allocation | |
| Enhanced Operational Efficiency | - Streamlined processes and reduced cycle times |
| - Increased productivity and cost savings | |
| Proactive Risk Management | - Early identification and mitigation of risks and issues |
| - Improved compliance with regulatory requirements | |
| Opportunity Identification | - Capitalization on emerging business opportunities |
| - Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty |
In summary, real-time insights provided by the SAP Financial System and BW enable organizations to make better decisions, optimize performance, and gain a competitive edge in today's fast-paced and dynamic business environment. The role of the SAP FICO consultant is critical in ensuring that clients have accurate, reliable, and actionable insights that empower them to achieve their strategic objectives and drive sustainable growth.
Manual Data Entry
Manual data entry in the SAP Financial System may be necessary in various scenarios, such as during initial system implementation, data migration, or when making adjustments to master data or control tables. Here are some examples:
-
Initial Data Migration: During the initial implementation of the SAP Financial System, data from legacy systems or external sources may need to be manually entered into the SAP system to populate master data, transactional data, and configuration settings.
-
Master Data Maintenance: Updates or additions to master data elements such as cost centers, profit centers, GL accounts, or vendor/customer records may require manual data entry to reflect changes in business processes or organizational structures.
-
Transactional Data Correction: In cases where errors or discrepancies are identified in transactional data, manual adjustments may be necessary to correct the data and ensure accurate financial reporting and analysis.
-
Control Table Updates: Manual updates to control tables, configuration settings, or custom fields within the SAP system may be needed to accommodate changes in business rules, regulatory requirements, or system enhancements.
The outcomes and benefits of manual data entry in the SAP Financial System include:
| Outcome | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Data Accuracy | - Ensure accurate and reliable financial reporting |
| - Minimize errors and discrepancies in financial data | |
| Process Flexibility | - Adapt to changes in business processes and requirements |
| - Support customization and configuration flexibility | |
| Compliance and Audit Readiness | - Maintain compliance with regulatory requirements |
| - Facilitate audit trail and transparency of data changes | |
| Timely Data Availability | - Enable timely decision-making and analysis |
| - Support real-time reporting and performance monitoring |
To ensure the accuracy and integrity of manually entered data, the SAP Financial System provides various edit controls and validation mechanisms:
-
Data Validation Rules: The system allows the definition of data validation rules and checks to ensure that manually entered data meets predefined criteria and conforms to business rules and standards.
-
Field-Level Controls: Field-level controls can be configured to enforce data formatting, data ranges, and mandatory field requirements, preventing invalid or incomplete data entry.
-
Authorization and Approval Workflow: Role-based access controls and approval workflows can be implemented to enforce segregation of duties (SoD) and ensure that manual data entries are reviewed and approved by authorized personnel before being finalized.
-
Audit Trail and Logging: The system logs all data changes and maintains an audit trail of manual entries, including details such as user IDs, timestamps, and the nature of the changes made. This enhances transparency and accountability in data management processes.
The role of the SAP FICO consultant in configuring these controls is essential:
- The consultant works closely with stakeholders to understand business requirements, data governance policies, and compliance standards related to manual data entry.
- They configure the SAP system settings, data validation rules, and authorization controls to enforce data integrity and prevent unauthorized or erroneous data entry.
- The consultant conducts user training and provides guidance on data entry best practices, error correction procedures, and audit trail review to ensure data accuracy and compliance with regulatory requirements.
By configuring robust edit controls and validation mechanisms, the SAP FICO consultant helps mitigate the risk of data errors, ensure data integrity, and enhance the reliability and trustworthiness of financial information within the SAP Financial System.
Financial Data Transfers
Financial data transfers from the SAP system outbound to external systems play a crucial role in various financial operations, especially in industries like Financial Services where real-time pricing of bonds and forex is essential. Here are some examples where outbound data transfers may occur:
-
Bond Pricing Updates: Financial institutions may need to transfer updated bond pricing data from the SAP system to trading platforms or market data providers to reflect changes in market conditions, interest rates, or bond yields.
-
Forex Rates Updates: Organizations involved in foreign exchange trading or international transactions may transfer updated forex rates from the SAP system to trading platforms, treasury systems, or third-party forex providers to facilitate currency conversions and hedging strategies.
-
Portfolio Management: Investment firms and asset managers may transfer portfolio data, including asset allocations, holdings, and performance metrics, from the SAP system to portfolio management systems, risk analytics platforms, or client reporting tools for portfolio analysis and reporting.
-
Risk Management: Risk management systems may receive data feeds from the SAP system containing information on market risk factors, credit risk exposures, counterparty exposures, and regulatory compliance metrics to support risk modeling, stress testing, and regulatory reporting.
Best Practices for setting up outbound financial data transfers include:
-
Real-Time Data Streaming: Leverage SAP HANA's in-memory computing capabilities to stream real-time financial data outbound to external systems, ensuring fast and reliable data delivery for time-sensitive operations such as bond pricing and forex trading.
-
Data Encryption and Secure Transmission: Implement robust encryption standards and secure transmission protocols (e.g., SSL/TLS) to protect sensitive financial data during outbound transfers and minimize the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
-
Data Quality and Accuracy Checks: Perform data quality checks and validation routines to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of outbound financial data transferred from the SAP system, reducing the risk of errors and discrepancies downstream.
-
Error Handling and Logging: Implement error handling mechanisms and logging functionality to capture and track outbound data transfer errors, exceptions, and data reconciliation discrepancies, enabling timely resolution and audit trail review.
-
Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: Ensure outbound data transfers comply with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and data privacy regulations governing financial data sharing, transmission, and disclosure, especially in highly regulated industries like Financial Services.
-
Monitoring and Performance Optimization: Implement monitoring tools and performance optimization techniques to track the latency, throughput, and reliability of outbound data transfers from the SAP system, identifying bottlenecks and optimizing data transfer processes for maximum efficiency and scalability.
By following these best practices, organizations in the Financial Services industry can effectively manage outbound financial data transfers from the SAP system, ensure data accuracy and integrity, and support mission-critical financial operations such as bond pricing, forex trading, and portfolio management with confidence and reliability.
Data Inconsistencies
Data inconsistencies in the SAP Financial System can have significant implications for accurate financial reporting, tax compliance, and operational efficiency. The SAP FICO consulting team plays a crucial role in configuring the system to prevent data inconsistencies and ensure the integrity of financial data. Here's a step-by-step diagnostic process for identifying and correcting data inconsistencies:
-
Data Analysis and Profiling:
- The consulting team conducts a comprehensive analysis and profiling of financial data stored in the SAP system, identifying inconsistencies, anomalies, and discrepancies across various data elements such as GL accounts, cost centers, profit centers, and vendor/customer records.
- Data profiling tools and techniques are used to assess data quality, completeness, and consistency, highlighting areas of concern and potential data integrity issues.
-
Root Cause Analysis:
- The team performs root cause analysis to identify the underlying factors contributing to data inconsistencies, including data entry errors, system configuration issues, data migration issues, and integration problems with other SAP modules or external systems.
- Interviews with key stakeholders, process walkthroughs, and system reviews help uncover the root causes of data inconsistencies and determine corrective actions.
-
System Configuration Review:
- The team reviews the system configuration settings, master data maintenance procedures, and transaction processing controls within the SAP Financial System to identify areas where data inconsistencies may arise due to configuration errors or insufficient controls.
- Configuration settings related to validation rules, field-level controls, authorization checks, and master data governance are evaluated to ensure alignment with best practices and regulatory requirements.
-
Data Validation and Error Handling:
- The team assesses the effectiveness of data validation mechanisms and error handling processes within the SAP system for detecting and resolving data inconsistencies in real-time.
- Validation rules, input masks, and data validation checks are reviewed to ensure they are comprehensive, accurate, and aligned with business rules and requirements.
-
Process Improvement Recommendations:
- Based on the findings of the diagnostic process, the consulting team develops recommendations for process improvements, system enhancements, and data governance practices to prevent data inconsistencies in the future.
- Recommendations may include streamlining data entry processes, implementing automated validation checks, enhancing user training and awareness, and strengthening controls over master data maintenance and transaction processing.
-
Implementation and Monitoring:
- The team works collaboratively with stakeholders to implement the recommended changes and improvements to address data inconsistencies and enhance data integrity within the SAP Financial System.
- Ongoing monitoring and performance tracking mechanisms are established to measure the effectiveness of the corrective actions and ensure sustained improvements over time.
Examples of data inconsistencies that may prompt CFOs to engage SAP FICO experts include:
- Duplicate GL account entries leading to inaccurate financial statements.
- Inconsistent cost center mappings causing misallocation of expenses.
- Incorrect tax codes resulting in compliance issues and penalties.
- Incomplete vendor/customer records leading to payment processing errors.
- Inaccurate inventory valuations impacting profitability analysis and inventory management.
By following a systematic diagnostic process and leveraging the expertise of SAP FICO consultants, organizations can identify and correct data inconsistencies in the SAP Financial System, ensuring accurate financial reporting, compliance with regulatory requirements, and effective decision-making.
Our SAP FICO Consultants
How Can Our SAP FICO Consultants Help?
Whether you need help implementing new SAP Finance and Controlling modules, additional support optimizing your accounting business processes, an extra hand conducting SAP FICO training for your internal employees, or anything else in between, SAP BW Consulting, Inc., is here to help.
SAP FICO End-to-End Implementation Process
Our SAP FICO consultants have the skills and experience needed to solve even the most complex SAP implementation, documentation, and configuration issues and help your team get the most out of your SAP investment. They can help you. with the complete SAP FICO end to end implementation process.
Contact us today to learn more about our SAP consulting services and the ways our team can help you.
Featured Articles
Hire a PPC Consultant
How Do You Easily Choose the Right Google PPC Consultant to Hire?
Geotargeting and Local Advertising
Mastering Geotargeting and Local Advertising for Google Ads Success
Schedule a Consult
In order to see if we are the right fit for your business, schedule a call with one of our strategists.
What Our Customers Say About Us

Elizabeth Sanjenis, Sr. IT Global Sales and Marketing Business Analyst, Johnson Controls
Working with Lonnie was a wonderful surprise in my career. Not only is he a passionate Marketing professional, but a great team member and employee with more than a "can-do" attitude, but rather a "we will" conviction. With his help and strategic expertise in SEO and Inbound Marketing, we were able to improve our website's lifetime visits count from 2.37 million in two years, to 1 million visitors per month. He also helped boost our shopping cart conversion rate from 7 to 13 percent, and implemented YouTube best practices that helped raise our subscriber count from about 1k to 21k, among other multiple contributions, which helped our company reach unprecedented increases in revenue. He is a very powerful addition to any strategic digital marketing team and I sincerely look forward to the opportunity of working with him in the future again.

Soren Detering, Detering Consulting
Working with Lonnie Ayers of SAP BW Consulting, Inc. has helped me grow my SAP practice to multi 8 figure SAP consulting engagements. I've also become an official SAP Partner and refined and perfected my Sales approach.

General Manager WW Strategic Sales Dynamics365 at MicrosoftRome Area, Italy
Working with Lonnie represented for me an extraordinary chance to increase my knowledge into the Airline MRO Operation. Lonnie is great to understand industry trends and issue issues and match those with customer request and advising the customer on who SAP solution provide support. Lonnie is a very proactive professional with an entrepreneur mindset.
Featured in











